Inverse Mie Theory Functions¶
Contour Intersection Inversion Functions¶
For more details on the contour intersection inversion method, please see Sumlin BJ, Heinson WR, Chakrabarty RK. Retrieving the Aerosol Complex Refractive Index using PyMieScatt: A Mie Computational Package with Visualization Capabilities. J. Quant. Spectros. Rad. Trans. 2017. DOI: 10.1016/j.jqsrt.2017.10.012 There’s also a good example here.
-
ContourIntersection(Qsca, Qabs, wavelength, diameter[, n=None, k=None, nMin=1, nMax=3, kMin=0.00001, kMax=1, Qback=None, gridPoints=100, interpolationFactor=2, maxError=0.005, fig=None, ax=None, axisOption=0])¶ Computes complex m = n+ik from a particle diameter (in nm), incident wavelength (in nm), and scattering and absorption efficiencies. Optionally, backscatter efficiency may be specified to constrain the problem to produce a unique solution.
Parameters
- Qsca : float or list-like
- The scattering efficiency, or optionally, a list, tuple, or numpy.ndarray of scattering efficiency and its associated error.
- Qabs : float or list-like
- The absorption efficiency, or optionally, a list, tuple, or numpy.ndarray of absorption efficiency and its associated error..
- wavelength : float
- The wavelength of incident light, in nm.
- diameter : float
- The diameter of the particle, in nm.
- n : float or list-like, optional
- An assumed real refractive index. Can be used in case scattering data is not available. If specified as a list, it must have only two elements. The first is the assumed n and the second is an uncertainty, such as a standard deviation.
- k : float or list-like, optional
- An assumed imaginary refractive index. Useful if only considering nonabsorbing aerosols, so you can set k=0. If specified as a list, it must have only two elements. The first is the assumed k and the second is an uncertainty, such as a standard deviation. **Note: when specifying this in the function call, input it as a real number. Omit the imaginary unit.
- nMin : float, optional
- The minimum value of n to search.
- nMax : float, optional
- The maximum value of n to search.
- kMin : float, optional
- The minimum value of k to search.
- kMax : float, optional
- The maximum value of k to search.
- Qback : float or list-like, optional
- The backscatter efficiency, or optionally, a list, tuple, or numpy.ndarray of backscatter efficiency and its associated error.
- gridPoints : int, optional
- The number of gridpoints for the search mesh. Defaults to 200. Increase for better resolution but longer run times.
- interpolationFactor : int, optional
- The interpolation to apply to the search fields, artificially increasing their resolutions. This is applied after calculations, so some features may be lost if interpolationFactor is too high and gridPoints is too low.
- maxError : float, optional
- The allowed error in forward calculations of the retrived m.
- fig : matplotlib.figure object, optional (but recommended)
- The figure object to send to the geometric inversion routine. If unspecified, one will be created.
- ax : matplotlib.axes object, optional (but recommended)
- The axes object to send to the geometric inversion routine. If unspecified, one will be created.
- axisOption : int, optional
Dictates the axis scales. Kind of useless since version 1.3.0. It’s still around until I get rid of it. Acceptable parameters are:
- ‘0’ for automatic detection of best axis scaling
- ‘1’ for linear axes
- ‘2’ for linear x and logarithmic y
- ‘3’ for logarithmic x and linear y
- ‘4’ for log-log
Returns
- solutionSet : list
- A list of all valid solutions
- ForwardCalculations : list
- A list of scattering and absorption efficencies produced by forward Mie calculations using the derived refractive indices
- solutionErrors : list
- The relative errors of the efficencies in ForwardCalculations.
- fig : matplotlib.figure object
- The figure object now associated with the inversion calculations.
- ax : matplotlib.axes object
- The axes object now associated with the inversion calculations.
- graphElements : dict
A dict of all artists necessary to fully manipulate the appearance of the output. The keys will depend on the options passed to the inversion function itself (i.e., errors specified, backscatter specified). Maximally, it will contain:
- ‘Qsca’, ‘Qabs’, ‘Qback’ - the major contours;
- ‘QscaErrFill’, ‘QscaErrOutline1’, ‘QscaErrOutline2’ - the error bound contours;
- ‘QabsErrFill’, ‘QabsErrOutline1’, ‘QabsErrOutline2’ - the error bound fills;
- ‘SolMark’, ‘SolFill’ - the circle thingies at each solution;
- ‘CrosshairsH’, ‘CrosshairsV’ - solution crosshairs;
- ‘LeftSpine’, ‘RightSpine’, ‘BottomSpine’, ‘TopSpine’ - graph spines;
- ‘XAxis’, ‘YAxis’ - the individual matplotlib axis objects.
-
ContourIntersection_SD(Bsca, Babs, wavelength, dp, ndp[, n=None, k=None, nMin=1, nMax=3, kMin=0.00001, kMax=1, SMPS=True, Bback=None, gridPoints=100, interpolationFactor=2, maxError=0.005, fig=None, ax=None, axisOption=0])¶ Computes effective complex m = n+ik from a measured or constructed size distribution (in cm-3), incident wavelength (in nm), and scattering and absorption coefficients (in Mm-1). Optionally, backscatter coefficient may be specified to constrain the problem to produce a unique solution.
Parameters
- Bsca : float or list-like
- The scattering coefficient, or optionally, a list, tuple, or numpy.ndarray of scattering coefficient and its associated error.
- Babs : float or list-like
- The absorption coefficient, or optionally, a list, tuple, or numpy.ndarray of absorption coefficient and its associated error..
- wavelength : float
- The wavelength of incident light, in nm.
- dp : list-like
- The diameter bins of the size distribution, in nm.
- ndp : list-like
- The number of particles per diameter bin corresponding to dp, in cm-3. Must be same length as dp.
- n : float or list-like, optional
- An assumed real refractive index. Can be used in case scattering data is not available. If specified as a list, it must have only two elements. The first is the assumed n and the second is an uncertainty, such as a standard deviation.
- k : float or list-like, optional
- An assumed imaginary refractive index. Useful if only considering nonabsorbing aerosols, so you can set k=0. If specified as a list, it must have only two elements. The first is the assumed k and the second is an uncertainty, such as a standard deviation. **Note: when specifying this in the function call, input it as a real number. Omit the imaginary unit.
- nMin : float, optional
- The minimum value of n to search.
- nMax : float, optional
- The maximum value of n to search.
- kMin : float, optional
- The minimum value of k to search.
- kMax : float, optional
- The maximum value of k to search.
- SMPS : bool, optional
- The switch determining the source of the size distribution data. Omit or set to
Truefor laboratory measurements, set toFalsefor analytical distributions. - Bback : float or list-like, optional
- The backscatter coefficient, or optionally, a list, tuple, or numpy.ndarray of backscatter coefficient and its associated error.
- gridPoints : int, optional
- The number of gridpoints for the search mesh. Defaults to 200. Increase for better resolution but longer run times.
- interpolationFactor : int, optional
- The interpolation to apply to the search fields, artificially increasing their resolutions. This is applied after calculations, so some features may be lost if interpolationFactor is too high and gridPoints is too low.
- maxError : float, optional
- The allowed error in forward calculations of the retrived m.
- fig : matplotlib.figure object, optional (but recommended)
- The figure object to send to the geometric inversion routine. If unspecified, one will be created.
- ax : matplotlib.axes object, optional (but recommended)
- The axes object to send to the geometric inversion routine. If unspecified, one will be created.
- axisOption : int, optional
Dictates the axis scales. Kind of useless since version 1.3.0. It’s still around until I get rid of it. Acceptable parameters are:
- ‘0’ for automatic detection of best axis scaling
- ‘1’ for linear axes
- ‘2’ for linear x and logarithmic y
- ‘3’ for logarithmic x and linear y
- ‘4’ for log-log
Returns
- solutionSet : list
- A list of all valid solutions
- ForwardCalculations : list
- A list of scattering and absorption coefficients produced by forward Mie calculations using the derived effective refractive indices
- solutionErrors : list
- The relative errors of the coefficients in ForwardCalculations.
- fig : matplotlib.figure object
- The figure object now associated with the inversion calculations.
- ax : matplotlib.axes object
- The axes object now associated with the inversion calculations.
- graphElements : dict
A dict of all artists necessary to fully manipulate the appearance of the output. The keys will depend on the options passed to the inversion function itself (i.e., errors specified, backscatter specified). Maximally, it will contain:
- ‘Bsca’, ‘Babs’, ‘Bback’ - the major contours;
- ‘BscaErrFill’, ‘BscaErrOutline1’, ‘BscaErrOutline2’ - the error bound contours;
- ‘BabsErrFill’, ‘BabsErrOutline1’, ‘BabsErrOutline2’ - the error bound fills;
- ‘SolMark’, ‘SolFill’ - the circle thingies at each solution;
- ‘CrosshairsH’, ‘CrosshairsV’ - solution crosshairs;
- ‘LeftSpine’, ‘RightSpine’, ‘BottomSpine’, ‘TopSpine’ - graph spines;
- ‘XAxis’, ‘YAxis’ - the individual matplotlib axis objects.
Survey-iteration Inversion Functions¶
The survey-iteration inversion algorithm is discussed in detail in the Supplementary Material of the JQSRT paper. It is a strictly numerical two phase algorithm. First, a low-resolution survey of n-k space is conducted and values of efficiencies or coefficients close to the inputs are located. From this survey, candidate m values are determined. The iteration phase is best described by this flowchart:
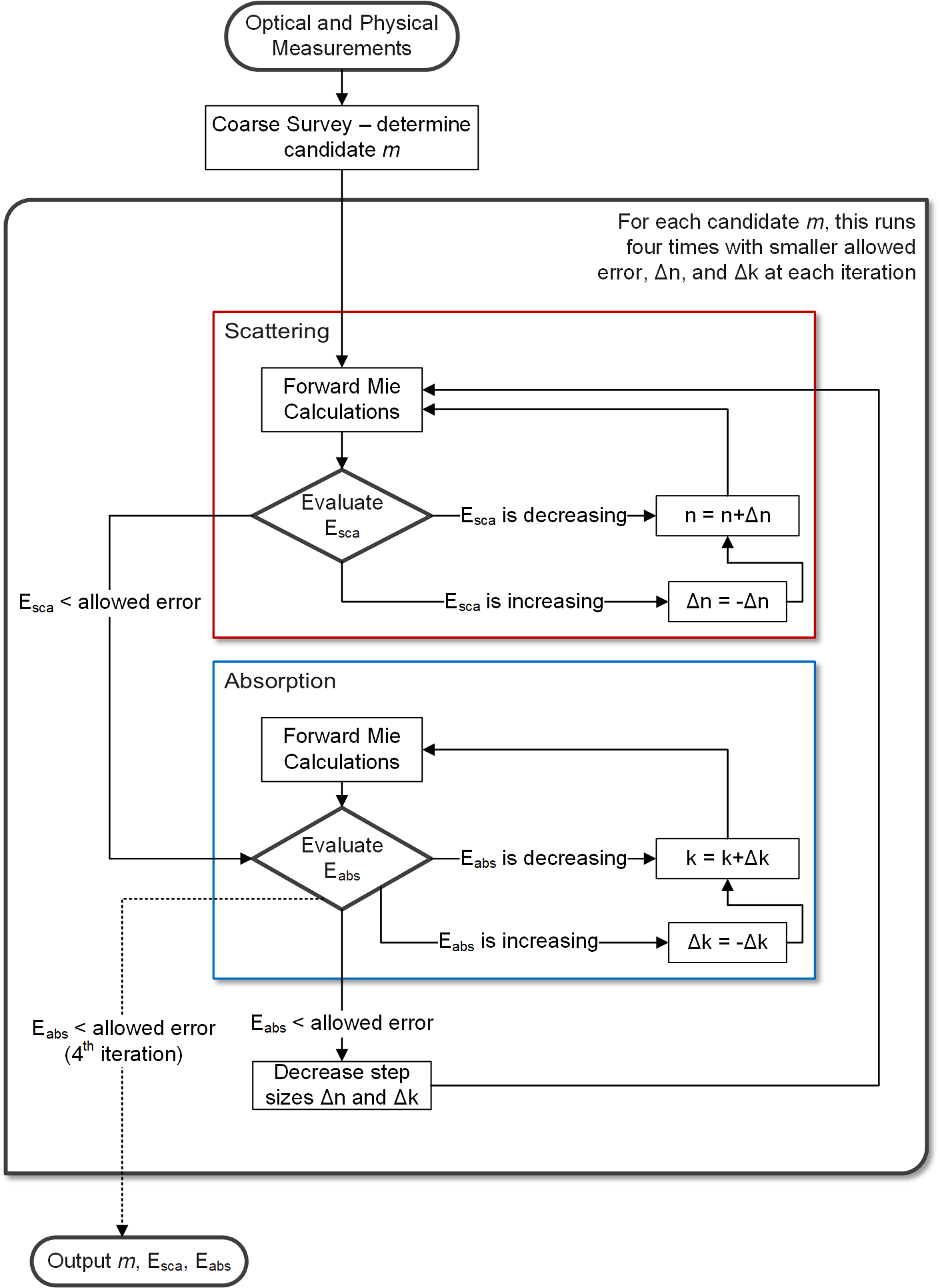
-
SurveyIteration(Qsca, Qabs, wavelength, diameter[, tolerance=0.0005])¶ Computes complex m=n+ik for given scattering and absorption efficencies, incident wavelength, and particle diameter.
Parameters
- Qsca : float
- Measured scattering efficiency.
- Qabs : float
- Measured absorption efficiency.
- wavelength : float
- The incident wavelength of light, in nm.
- diameter : float
- The particle diameter in nm.
- tolerance : float, optional
- The maximum error allowed in forward Mie calculations of retrieved indices.
Returns
- resultM : list-like
- The retrieved refractive indices. Be sure and scrutinize this list for repeat entries.
- resultScaErr : list-like
- The relative error in scattering efficiency for each retrieved m.
- resultAbsErr : list-like
- The relative error in absorption efficiency for each retrieved m.
-
SurveyIteration_SD(Bsca, Babs, wavelength, dp, ndp[, tolerance=0.0005, SMPS=True])¶ Computes complex m=n+ik for given scattering and absorption coefficients, incident wavelength, and particle diameter.
Parameters
- Qsca : float
- Measured scattering coefficient.
- Qabs : float
- Measured absorption coefficient.
- wavelength : float
- The incident wavelength of light, in nm.
- dp : list-like
- The particle diameter bins in nm.
- ndp : list-like
- The particle concentrations (in cm-3) corresponding to each of the bins in dp.
- tolerance : float, optional
- The maximum error allowed in forward Mie calculations of retrieved indices.
- SMPS : bool, optional
- The switch determining the source of the size distribution data. Omit or set to
Truefor laboratory measurements, set toFalsefor analytical distributions.
Returns
- resultM : list-like
- The retrieved refractive indices. Be sure and scrutinize this list for repeat entries.
- resultScaErr : list-like
- The relative error in scattering coefficient for each retrieved m.
- resultAbsErr : list-like
- The relative error in absorption coefficient for each retrieved m.